Patients or post-operative patients, high load and high intensity exercises may not be clinically proper.
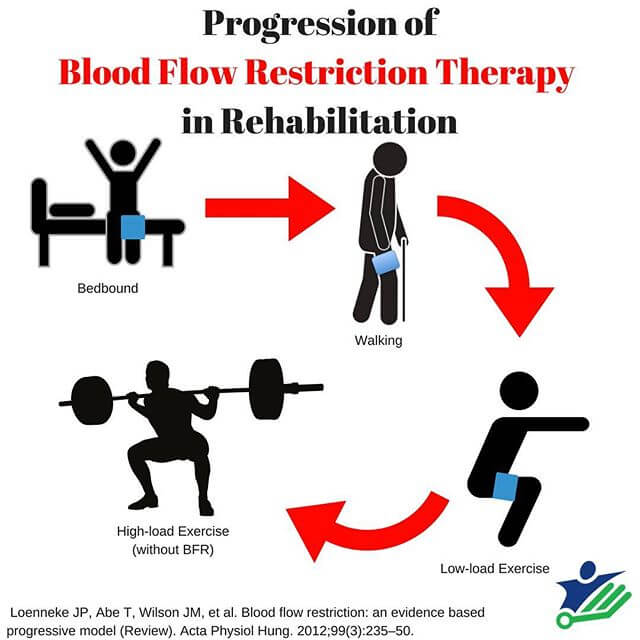
Blood Circulation Limitation (BFR) training is a technique that combines low strength workout with blood circulation occlusion that produces similar results to high strength training. It has actually been used in the fitness center setting for a long time however it is getting popularity in clinical settings. Blood Circulation Constraint (BFR) Training [edit modify source] BFR training was initially established in the 1960's in Japan and known as KAATSU training.
It can be applied to either the upper or lower limb. The cuff is then inflated to a particular pressure with the aim of obtaining partial arterial and total venous occlusion. The patient is then asked to carry out resistance workouts at a low strength of 20-30% of 1 repetition max (1RM), with high repeatings per set (15-30) and short rest intervals between sets (30 seconds) Understanding the Physiology of Muscle Hypertrophy. [modify modify source] Muscle hypertrophy is the boost in size of the muscle in addition to an increase of the protein content within the fibers.
Muscle tension and metabolic tension are the 2 primary aspects responsible for muscle hypertrophy. Mechanical Tension & Metabolic Tension [modify edit source] When a muscle is put under mechanical stress, the concentration of anabolic hormonal agent levels increase. The activation of myogenic stem cells and the elevated anabolic hormonal agents lead to protein metabolism and as such muscle hypertrophy can take place.
Insulin-like development factor and development hormonal agent are responsible for increased collagen synthesis after exercise and help muscle healing. Development hormone itself does not straight trigger muscle hypertrophy however it aids muscle healing and thus possibly assists in the muscle strengthening procedure. The accumulation of lactate and hydrogen ions (eg in hypoxic training) additional increases the release of growth hormone.
Myostatin controls and hinders cell development in muscle tissue. It requires to be essentially shut down for muscle hypertrophy to occur. Resistance training results in the compression of capillary within the muscles being trained. This triggers an hypoxic environment due to a decrease in oxygen delivery to the muscle.
When there is blood pooling and a build-up of metabolites cell swelling takes place. This swelling within the cells causes an anabolic response and results in muscle hypertrophy.
The cuff is put proximally to the muscle being workout and low intensity exercises can then be carried out. Since the outflow of blood is restricted utilizing the cuff capillary blood that has a low oxygen material collects and there is a boost in protons and lactic acid. The exact same physiological adaptations to the muscle (eg release of hormones, hypoxia and cell swelling) will happen during the BFR training and low strength workout as would accompany high intensity exercise.
( 1) Low strength BFR (LI-BFR) leads to a boost in the water material of the muscle cells (cell swelling). It likewise speeds up the recruitment of fast-twitch muscle fibres. It is likewise hypothesized that when the cuff is removed a hyperemia (excess of blood in the blood vessels) will form and this will trigger further cell swelling.
These boosts were similar to gains acquired as an outcome of high-intensity exercise without BFR A research study comparing (1) high strength, (2) low strength, (3) high and low strength with BFR and (4) low strength with BFR. While all 4 exercise regimes produced increases in torque, muscle activations and muscle endurance over a 6 week duration - the high intensity (group 1) and BFR (groups 3 and 4) produced the best impact size and were similar to each other.